Milk Protein Concentrate | MPC
Dairytex
50% Protein
(min)
Formula 7+
70% Protein
(min)
Formula 8
78% Protein
(Not More Than)
Formula 8+
80% Protein
(min)
Sports
Functional
Sustainable
Milk Protein Concentrate | Protein Fortification
EnNutrica’s Milk protein Concentrate is Native Milk protein with Casein in Its Miscellar Form (Miscellar casein)
Our Milk protein concentrate “Formula” products are Native Milk protein in soluble form, Having the Non Denatured Miscellar Casein and whey Proteins, Prepared from fresh Skim Milk using Cold Filtration Process.
The Skimmed Milk is Cold Filtered to remove Lactose content Concentrating the Proteins Naturally.
No Chemical Process / Biological process is used.
As a result, The Proteins are in the Native Bio Available Form.
Milk Protein Concentrate
- Made by Cold Filtration process of skimmed milk
- Contains intact Miscellar Casein & Whey at the Natural ratio of 80:20
- Contains Proteins in the Most Native and Bioavailable form
Typical Application
Milk protein Concentrates MPCs are currently used for manufacturing products, including: process cheese, cream cheese, ice cream, yogurt/fermented dairy and meal replacement beverages. Application and formulation dictate the type of MPC used. Typically, lower-protein MPCs are used as ingredients in cheese applications, while higher-protein MPCs are used in beverage and bar applications. They are used as an ingredient in applications that rely on nonfat dry milk/skim milk powder but require a higher level of protein where casein and caseinate are used traditionally.
Milk Protein Concentrate 70% is Soluble Native Milk Protein, Prepared from Fresh Skim Milk by Cold Filtration Process.
Milk Protein Concentrate 70% | Formula 7+ is used in Nutrition Products and Dairy Products for Protein Fortification and Milky Taste. It has 70 % Protein and It can be used for Protein Enrichment of Nutrition Products, Supplement Products, Bars, Protein Beverages, Dairy Drinks, Breakfast Cereals and a wide variety of food products. It is also used as and Emulsifier or Stabilizer in Liquid Nutrition Formulas and Dairy Products. It also gives Excellent Mouth feel and taste making it the Ultimate Choice for Fortifying any Food Products.
Milk Protein Concentrate 78% & 80% | Formula 8, 8+ is Soluble Native Milk Proteins, Prepared from Fresh Skim Milk using Cold Filtration Process.
Milk Protein Concentrate 78% and 80% | Formula 8 and 8+ are used in Nutrition Products for its High Quality Native Milk Proteins with Protein content of 78% and 81% Respectively and has a bland protein rich tase. It can be used for Protein Enrichment of Nutrition Products, Supplement Products, Bars, Protein Beverages, Dairy Drinks, Breakfast Cereals and a wide variety of food products where High Protein percentage is Needed. It is also used as and Emulsifier or Stabilizer in Liquid Nutrition Formulas and Dairy Products. It also gives Excellent Mouth feel and taste making it the Ultimate Choice for Fortifying any Food Products.
Milk Protein Concentrate | MPC as Formula 7+, 8, 8+ by EnNutrica
How Milk Protein Concentrate work for Nutrition industry?
Milk protein Concentrate (MPC) s are complete dairy proteins that contain both casein and whey proteins. MPCs with higher concentrations of proteins can be used to enhance a products protein content without adding significant levels of lactose and contribute valuable minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus in the Best Absorbable form. The Amino Acid profile. Used By Many Nutritional Products For The Time Bound Release of Energy.
Since protein needs are a function of lean tissue mass, not calorie intake, protein requirements should be calculated in terms of body weight rather than as a percentage of calories. This is critical with lower energy intakes: When calorie intake is low and protein needs are calculated as a percentage of calories, the amount of protein may be inadequate. Moreover, when energy needs aren’t met, protein becomes an alternate fuel source, which may increase.
It Helps in Effective Weight reduction By Increasing Metabolism-Ref- Milk Protein for Improved Metabolic Health : A Review of the Evidence
How Milk protein Concentrate Helps in Protein Fortification & Achieve RDA ?
For optimal health, evidence shows all adults need more protein than previously thought. Protein is the major structural component of all cells in the body and functions in the form of enzymes, transport carriers, and hormones. The body requires a steady supply of the nine essential amino acids from dietary protein to synthesize new proteins and balance the rate of protein breakdown. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein, 0.8 g/kg of body weight per day for those aged 19 and older, is based on the minimal amount of protein required to prevent protein deficiency, not necessarily the optimal amount to promote health. The Institute of Medicines Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for protein goes from 0.8 to at least 2.5 g/kg of body weight per day (or 10% to 35% of total calories from protein).
Recent research shows that protein intake at levels above the RDA but within the AMDR may help achieve and maintain a healthful body weight by increasing satiety and thermogenesis (the energy required to digest, absorb, and dispose of the nutrients from food), and improving body composition, and it can play a role in the treatment and prevention of obesity, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and sarcopenia .2,6 One study found better weight maintenance and fat reductions in moderately obese subjects who consumed a low-fat, high-protein diet containing either casein or whey following a weight-loss program compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet.
What is the Energy release Pattern of Milk Protein Concentrate | Formula Range?
As Formula 7+, Formula 8 and Formula 8+ are Milk protein Concentrate s (MPC) has the Combined Natural cow milks protein ratio of 80 : 20 between casein and whey proteins, (not The Protein Content. As the protein content can be 50, 70 or as stated.)
The Combined Energy release Pattern of the Forrmula Range of Products from EnNutrica will Have the Pattern as Below
Milk Protein Concentrate | Energy Delivery pattern

What is the Advantage of Milk Protein Concentrate in Nutrition Industy?
As Milk protein Concentrate s (MPC) | Formula 7+, Formula 8 and Formula 8+ has the Combined Natural cow milks protein ratio of 80 : 20 between casein and whey proteins, (not The Protein Content. As the protein content can be 50, 70 or as stated.)
The Combined Energy release Pattern of the Forrmula Range of Products from EnNutrica will Have the best of Both Proteins as below
Milk Protein Concentrate
80% Casein Protein
20 % Whey Protein
The Natural ratio as in Cow Milk



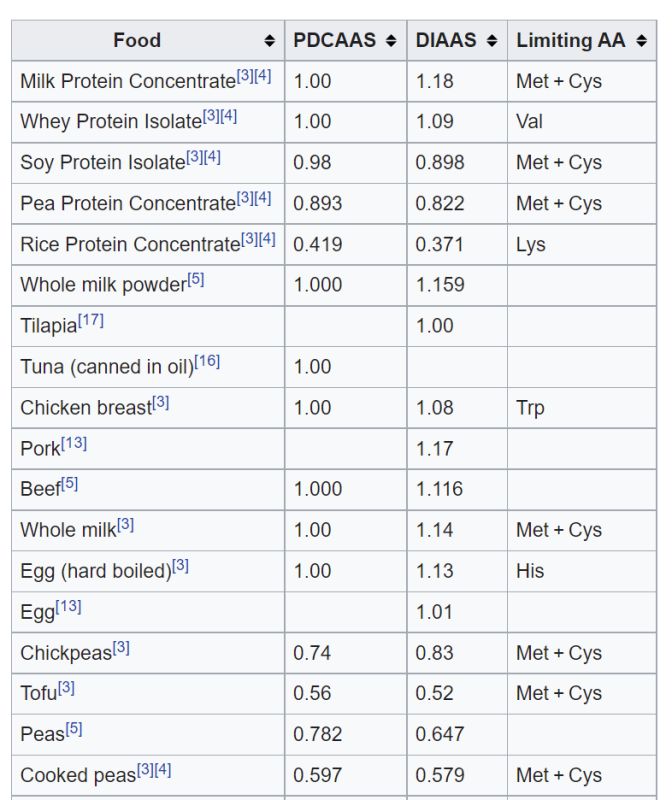
Milk Protein Concentrate has a PDCAAS Score of 1
Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans and their ability to digest it.
The PDCAAS rating was adopted by the US FDA and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) in 1993 as “the preferred ‘best'” method to determine protein quality.[1]
In 2013, FAO proposed changing to Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score.
Source : Wikipedia : Link
Abstract
Background: The FAO has recommended replacing the protein digestibility–corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) with the digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS).
Objective: The objective of this study was to compare aspects underlying the calculation of the DIAAS and PDCAAS, including 1) fecal digestibility vs. ileal digestibility, 2) using a single nitrogen digestibility value for all amino acids, and 3) the effect of truncation. Truncated PDCAAS and untruncated DIAAS values calculated as formally defined were also compared and DIAAS data presented for 14 dietary protein sources.
Methods: Semisynthetic wheat starch–based diets were formulated to contain the test protein (as consumed by humans) source (whey- and soy-protein isolates, milk-, whey-, rice- and pea- protein concentrates, cooked kidney beans, roasted peanuts, cooked peas, corn-based breakfast cereal, cooked rice, cooked rolled oats, and wheat bran) as the sole nitrogen source and with an indigestible marker (titanium dioxide). Growing male rats (∼250 g bodyweight) were given a basal casein-based diet from day 1 to day 7 and then allocated (n = 6) to the test diets for day 8 to day 14 before ileal digesta were collected after the rats were killed. Total feces were collected from day 11 to day 14.
Results: True fecal nitrogen digestibility was different (P < 0.05; 10% difference on average) from true ileal nitrogen digestibility for 11 of the 14 protein sources. True ileal nitrogen digestibility was different (P < 0.05) from true ileal amino acid digestibility for almost half of the indispensable and conditionally indispensable amino acids (differences ranged from 0.9% to 400%). DIAAS values ranged from 0.01 for a corn-based cereal to 1.18 for milk protein concentrate.
Conclusion: Untruncated PDCAAS values were generally higher than a DIAAS values, especially for the poorer quality proteins; therefore, the reported differences in the scores are of potential practical importance for populations in which dietary protein intake may be marginal.
Source: https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/145/2/372/4585766

DIAAS for Milk Protein Concentrate is 1.18
Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) is a protein quality method proposed in March 2013 by the Food and Agriculture Organization to replace the current protein ranking standard, the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS).
The DIAAS accounts for amino acid digestibility at the end of the small intestine, providing a more accurate measure of the amounts of amino acids absorbed by the body and the protein’s contribution to human amino acid and nitrogen requirements. This is in contrast to the PDCAAS, which is based on an estimate of digestibility over the total digestive tract. Values stated using this method generally overestimate the amount of amino acids absorbed.[1]
Dairy products are a particularly good and efficient source of protein. Keep in mind that it is more important to get a good balance of amino acids throughout the day by eating a varied diet, rather than necessarily ensuring all the amino acids are in every meal.
References:
Ertl, P., Knaus, W., Sollitsh, W. (2016) An approach to including protein quality when assessing the net contribution of livestock to human food supply. Animal. 10: 11, pp 1883-1889
FAO (2013) Dietary Protein Quality Evaluation in Human Nutrition. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 92. Link: http://www.fao.org/ag/humannutrition/35978-02317b979a686a57aa4593304ffc17f06.pdf
Moughan, P.J., Gilani, S., Rutherfurd, S.M., Tome, D. (2012) True ileal amino acid digestibility coefficients for application in the calculation of Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) in human nutrition. Report of a Sub-Committee of the 2011 FAO Consultation on “Protein Quality Evaluation in Human Nutrition” Link: http://www.fao.org/ag/humannutrition/36216-04a2f02ec02eafd4f457dd2c9851b4c45.pdf
Moughan, P.J., Butts, C.A., Wijk, Hv., Rowan, A.M., Reynolds, G.W. (2005) An Acute Ileal Amino Acid Digestibility Assay Is a Valid Procedure for Use in Human Ileostomates. J Nut. 135: 3, pp 404-409
Philips, S.M. (2017) Current Concepts and Unresolved Questions in Dietary Protein Requirements and Supplements in Adults. Front Nutr. 4: 13, pp 404-409
Source: https://www.mondoscience.com/blog/2017/10/25/100-amino-acid-score



Current Concepts and Unresolved
Questions in Dietary Protein Requirements
and Supplements in Adults
- April 2017
- Frontiers in Nutrition 4(13)
Phillips, Stuart. (2017). Current Concepts and Unresolved Questions in Dietary Protein Requirements and Supplements in Adults. Frontiers in Nutrition. 4. 10.3389/fnut.2017.00013.
Thermic Effect of Food
Thermic Effect (of Food) refers to the energy your body uses to digest, absorb, metabolize, and store nutrients after eating.
In simple words:
When you eat, your body burns calories just to process that food. That calorie burn is called the thermic effect.
Key points (short & clear):
- It accounts for about 8–10% of total daily energy expenditure
- Protein has the highest thermic effect (≈20–30%)
- Carbohydrates: ≈5–10%
- Fats: ≈0–3%
Why it matters:
- Higher protein intake slightly boosts metabolism
- Helps in weight management and muscle maintenance
- Important in performance and clinical nutrition
One-line proverb:
“Food that works harder to digest teaches the body to burn more.”
Thermic Effect of Milk Protein Concentrates
The Thermic Effect of Food (TEF) is the amount of energy the body uses to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients. Proteins have the highest thermic effect among all macronutrients.
Why Milk Proteins Are Important
Milk proteins—casein and whey, present together in Milk Protein Concentrates (MPC)—provide both immediate and sustained thermic activity.
How Different Milk Proteins Contribute
- Whey Protein
- Fast digestion and absorption
- Creates a rapid thermic response
- Supports muscle protein synthesis and metabolic activation
- Casein Protein
- Slow digestion and absorption
- Produces a prolonged thermic effect
- Supports satiety and overnight metabolism
- Milk Protein Concentrates (MPC)
- Contain natural ratio of casein and whey
- Deliver a dual-phase thermic effect (quick + sustained)
- Ideal for weight management, clinical nutrition, and performance products
Practical Nutrition Insight
Because milk proteins require more metabolic energy to process, they:
- Increase calorie burn after meals
- Improve satiety and appetite control
- Support lean muscle retention
- Enhance metabolic efficiency
One-line takeaway
“Milk proteins warm the metabolism twice—once fast, once slow.”
FAQ – Thermic Effect of Milk Proteins
- What is the thermic effect of food (TEF)?
Ans: The thermic effect of food is the energy the body uses to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients after eating.
- Why do proteins have a higher thermic effect than carbs or fats?
Ans: Proteins require more energy to break down into amino acids, making the body burn more calories during digestion.
- How do milk proteins contribute to the thermic effect?
Ans: Milk proteins contain both whey (fast-digesting) and casein (slow-digesting), creating a combined and sustained thermic response.
- What is the difference between whey and casein in thermic effect?
Ans: Whey produces a quick thermic response, while casein provides a slower, prolonged thermic effect.
- Why are Milk Protein Concentrates (MPC) effective for metabolism?
Ans: MPCs deliver the natural ratio of whey and casein, offering both immediate and sustained calorie-burning effects.
- Does a higher thermic effect help in weight management?
Ans: Yes. A higher thermic effect increases post-meal calorie burn and improves satiety, supporting weight control.
- Are milk proteins suitable for clinical and elderly nutrition?
Ans: Yes. Their sustained thermic effect and high digestibility make them ideal for medical and elderly nutrition.
- How does the thermic effect support muscle maintenance?
Ans: Higher protein digestion increases energy use while supplying amino acids for muscle repair and retention.
- Is MPC better than isolated proteins for thermic benefits?
Ans: Yes. MPC provides dual-phase digestion (fast + slow), whereas isolates offer only a single digestion pattern.
- Can thermic effect improve the performance of nutrition?
Ans: Yes. It supports recovery, metabolic efficiency, and lean muscle mass in active and athletic individuals.
Role of Milk Protein Concentrate with Hunger Hormone
Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC) plays a direct and indirect role in regulating hunger hormones, which is why it is widely used in weight management, clinical nutrition, and performance nutrition.
Below is a clear, science-aligned explanation you can use for technical discussions, presentations, or marketing (within compliance limits).
Key Hunger Hormones Involved
- Ghrelin – “Hunger hormone” (stimulates appetite)
- Leptin – “Satiety hormone” (signals fullness)
- CCK (Cholecystokinin) – promotes satiety
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) – reduces appetite, slows gastric emptying
- PYY (Peptide YY) – suppresses appetite
Role of Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC)
- Suppression of Ghrelin (Hunger Hormone)
MPC is rich in casein + whey proteins, which:
- Slow gastric emptying (especially casein)
- Prolong digestion time
- Reduce post-meal ghrelin secretion
Effect:
Reduced hunger signals
Longer feeling of fullness
- Stimulation of Satiety Hormones
MPC intake increases release of:
- CCK
- GLP-1
- PYY
These hormones:
- Signal fullness to the brain
- Reduce food intake in subsequent meals
Effect:
Better appetite control
Lower calorie intake naturally
- Protein-Induced Thermogenesis
MPC has a high thermic effect:
- Protein digestion uses more energy
- Increases post-meal thermogenesis
Effect:
Supports metabolic activity
Contributes to satiety through heat and energy expenditure
- Stabilization of Blood Glucose
MPC:
- Slows carbohydrate absorption
- Improves insulin response
Effect:
Prevents rapid blood sugar spikes and crashes
Reduces rebound hunger
- Amino Acid Signalling to the Brain
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), especially leucine, are present in MPC:
- Act on hypothalamic appetite centres
- Support satiety signalling pathways
Effect:
Central appetite regulation
Reduced desire for frequent eating
Casein vs Whey in MPC (Why MPC Is Special)
Component | Hunger Control Role |
Casein | Slow digestion, prolonged fullness |
Whey | Rapid satiety hormone release |
MPC (Both) | Immediate + sustained appetite control |
MPC offers dual-phase hunger regulation
Application Relevance
- Weight management & meal replacement
- Clinical nutrition (diabetes, obesity)
- Health & wellness supplements
- Performance nutrition (lean mass retention while cutting fat)
One-Line Scientific Summary
Milk Protein Concentrate helps regulate hunger by suppressing ghrelin, enhancing satiety hormones, stabilizing blood glucose, and increasing thermogenesis through its unique casein–whey protein matrix.
FSSAI / Marketing-Safe Claims for Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC)
General Permissible Positioning
Nutritional support
Satiety & fullness support
Appetite management support
Protein nutrition benefits
Approved-Style Claim Statements
Supports Satiety and Fullness
Milk Protein Concentrate provides high-quality milk proteins that help promote a feeling of fullness when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
- Helps in Appetite Management
The slow-digesting and fast-digesting proteins present in Milk Protein Concentrate support prolonged satiety, which may help manage appetite.
- Supports Normal Hunger Regulation
Protein-rich foods like Milk Protein Concentrate contribute to normal appetite regulation by supporting satiety-related physiological responses.
- Supports Sustained Energy Release
Milk Protein Concentrate is digested gradually, supporting sustained nutrient availability and helping avoid frequent hunger.
- Supports Metabolic Activity
Protein has a higher thermic effect compared to carbohydrates and fats, and Milk Protein Concentrate contributes to normal metabolic activity.
- Helps Maintain Lean Muscle Mass
Milk Protein Concentrate supports muscle maintenance when consumed along with regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
- Supports Blood Sugar Stability (Non-Medical)
Protein helps slow digestion and supports balanced nutrient absorption when consumed with meals.
Ingredient-Specific Safe Wording
Milk Protein Concentrate contains a natural balance of casein and whey proteins, offering both immediate and sustained nutritional support.
FAQs: Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC) & Hunger Support
- What is Milk Protein Concentrate (MPC)?
Milk Protein Concentrate is a high-quality dairy ingredient made from milk, containing a natural balance of casein and whey proteins. It is commonly used in health, nutrition, and food products for its nutritional value.
- How does Milk Protein Concentrate help with feeling full?
Milk Protein Concentrate is rich in protein, which is known to promote satiety. Protein takes longer to digest compared to carbohydrates, helping you feel full for a longer time after consumption.
- Does Milk Protein Concentrate control hunger hormones?
Milk Protein Concentrate does not control or alter hormones directly. However, as a protein-rich food, it supports normal appetite regulation and satiety responses in the body when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
- Can MPC help reduce frequent snacking?
Protein helps provide longer-lasting fullness, which may help reduce the desire to eat frequently between meals when included in a well-balanced diet.
- Why is protein important for appetite management?
Protein is known to:
- Promote satiety
- Support slower digestion
- Help maintain steady energy levels
These factors together support better appetite management.
- What makes MPC different from other protein sources?
Milk Protein Concentrate contains both fast-digesting whey and slow-digesting casein, offering:
- Immediate satiety support
- Sustained fullness over time
This dual benefit makes MPC suitable for daily nutrition.
- Does MPC help with weight loss?
Milk Protein Concentrate is not a weight-loss product. However, its protein content supports satiety and muscle maintenance, which can be helpful when following a balanced diet and active lifestyle.
- Is MPC suitable for people focused on health and nutrition?
Yes. MPC is widely used in health, nutrition, and performance products because it provides high-quality protein that supports everyday nutritional needs.
- Can MPC be used in meal replacement or nutrition drinks?
Yes. Due to its satiety-supporting properties, MPC is commonly used in nutrition drinks, shakes, and meal-support products.
- Does MPC affect blood sugar levels?
Protein helps slow digestion and nutrient absorption when consumed with meals, which supports balanced energy release. MPC does not claim to treat or manage any medical condition.
- Is Milk Protein Concentrate safe for daily consumption?
Yes, when consumed within recommended levels as part of a balanced diet. Individuals with milk allergies should avoid dairy-based proteins.
- Who can benefit from MPC-based products?
MPC can be beneficial for:
- Adults focusing on balanced nutrition
- Individuals seeking sustained fullness
- Active individuals and fitness enthusiasts
- People looking for high-quality dairy protein
- Does MPC replace meals?
No. Milk Protein Concentrate is a nutritional ingredient, not a meal replacement, unless formulated specifically for that purpose by a food manufacturer.
- Can MPC be consumed at any time of the day?
Yes. MPC can be consumed as part of breakfast, between meals, or post-activity, depending on individual nutritional needs.
- Is Milk Protein Concentrate a medicine or supplement?
Milk Protein Concentrate is a food ingredient, not a medicine. It supports nutrition and wellness when included in a healthy lifestyle.
Compliance Disclaimer (Recommended)
This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. To be consumed as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.



